Exploring the Health Benefits of Quercetin
Quercetin, a natural flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and herbs, has attracted growing attention for its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective properties. As a versatile compound, it has been studied for its therapeutic potential across diverse health conditions, including cancer, diabetes, osteoporosis, and gynecological disorders. Recent research sheds light on its molecular mechanisms and clinical applications, paving the way for future developments in functional foods and supplements.
1. Quercetin and Cancer: Epigenetic Modulation

Quercetin’s anticancer potential lies in its ability to interfere with tumor progression by targeting DNA methylation, a key factor in carcinogenesis. By modulating processes such as proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis, quercetin demonstrates a capacity to disrupt cancer cell development.
However, challenges such as poor solubility, short half-life, and limited tumor targeting hinder its therapeutic use. Emerging approaches like nanodelivery systems aim to enhance quercetin’s bioavailability and tumor specificity, making it a promising candidate for future cancer treatments.
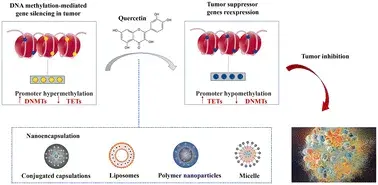
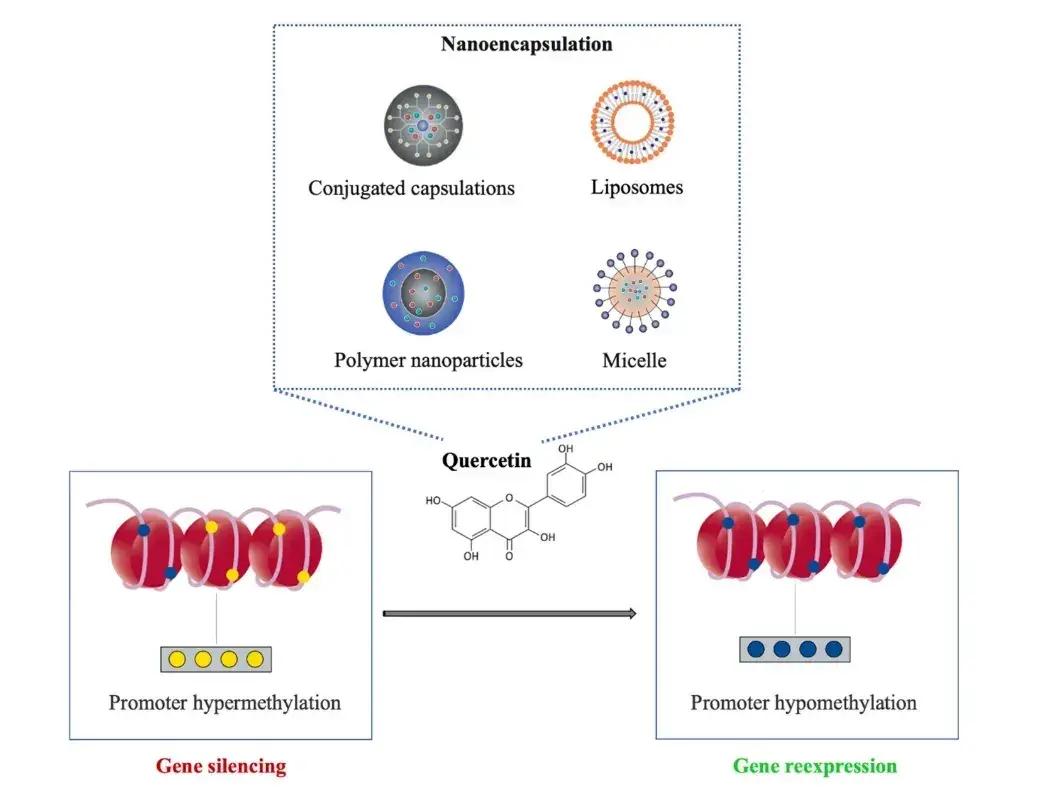
2. Quercetin Analogues in Diabetes Management

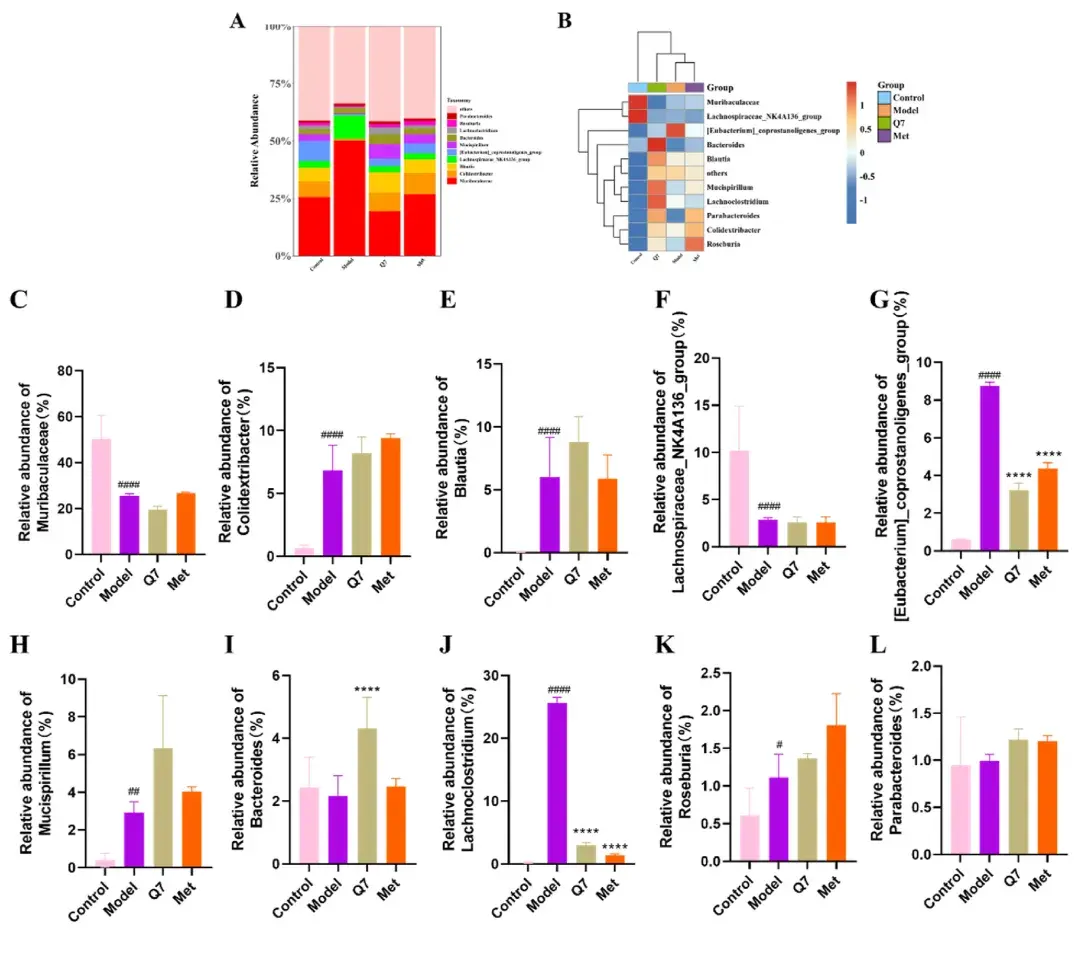
Quercetin and its synthetic analogue, Q7, exhibit potent α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, essential for controlling blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes. Studies reveal that Q7, enhanced with a unique -CF3 group, significantly reduces fasting blood glucose levels and modulates gut microbiota, improving anti-inflammatory responses and short-chain fatty acid production.
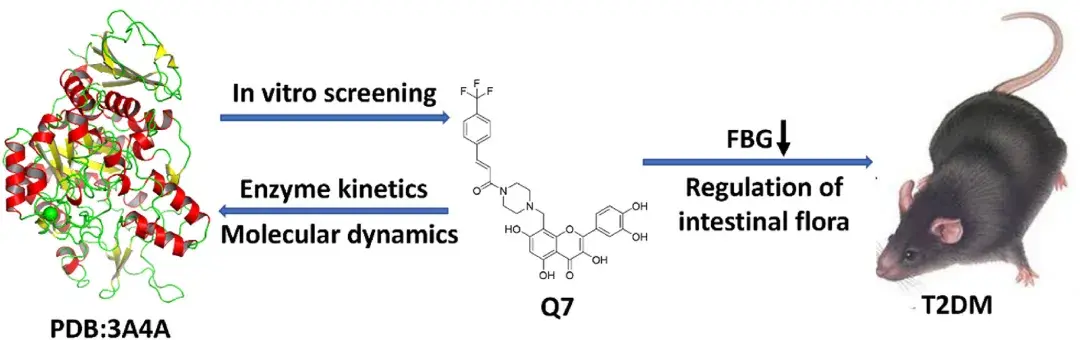
However, high doses of Q7 may disrupt carbohydrate metabolism in the colon, highlighting the need for precise dosage optimization to balance therapeutic efficacy and gut health.
3. Osteoporosis: The Gut-Bone Axis
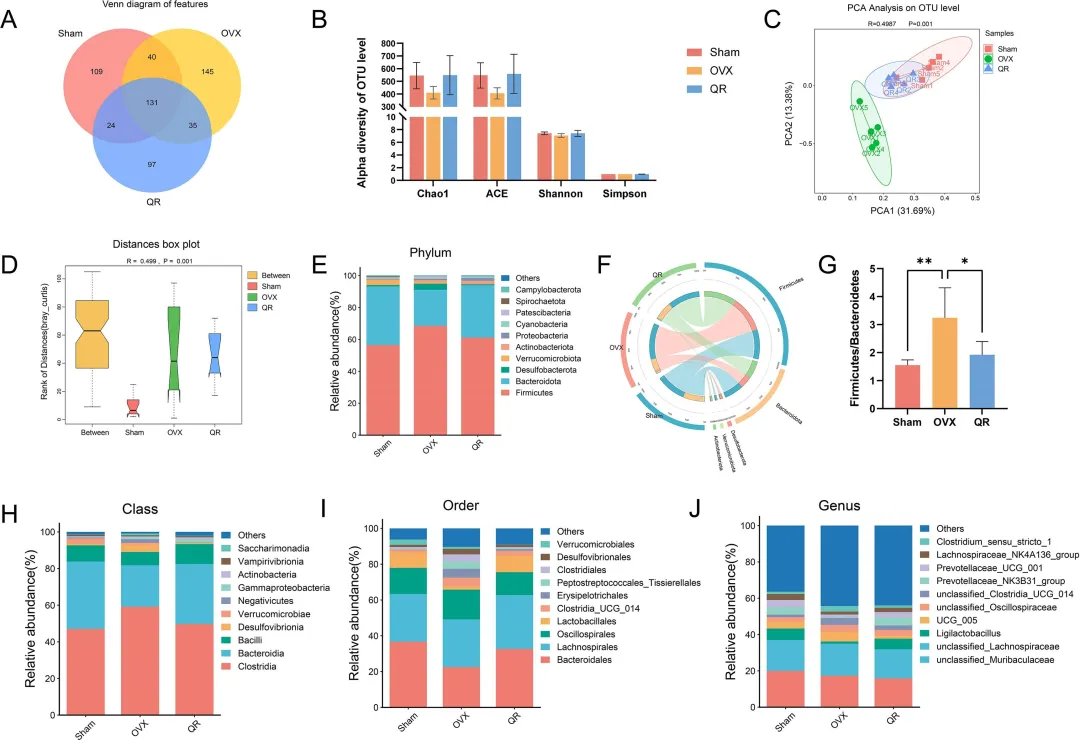
Quercetin plays a vital role in preventing bone loss, particularly in postmenopausal osteoporosis. In ovariectomized (OVX) rat models, quercetin supplementation enhances gut microbiota composition, increasing beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillales and Prevotellaceae.
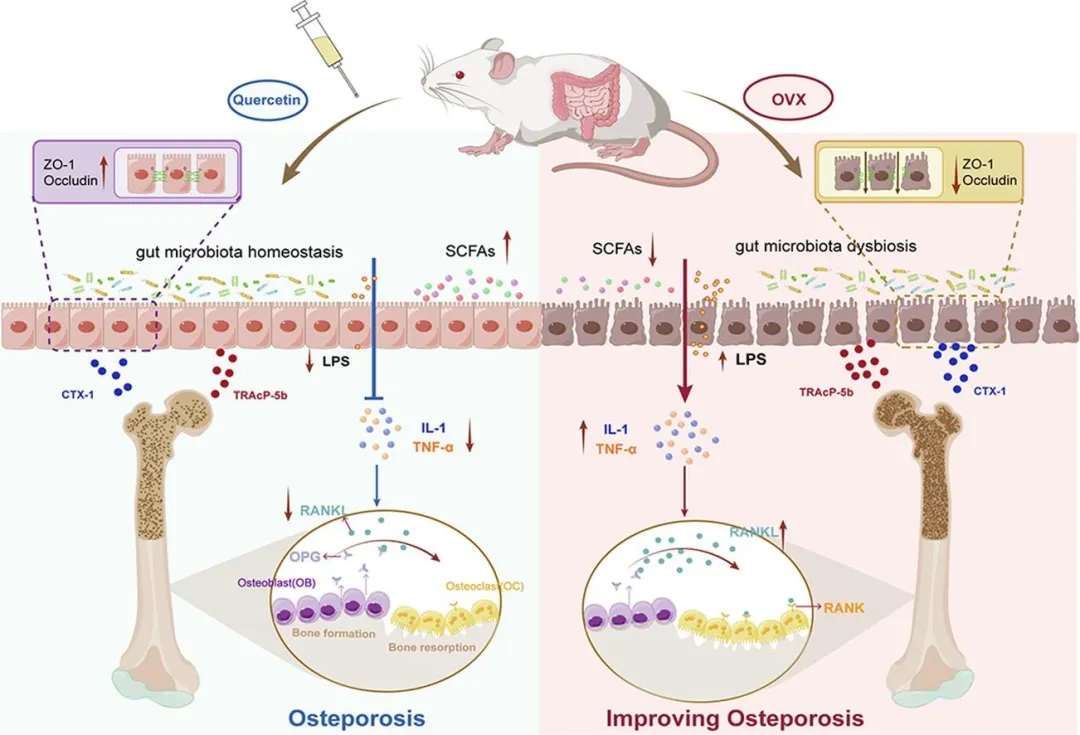
This regulation reduces gut permeability, elevates short-chain fatty acid levels, and suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines, ultimately improving bone density and strength. These findings underscore quercetin’s potential in modulating the gut-bone axis for osteoporosis prevention and treatment.
4. Gynecological Health: A Natural Remedy

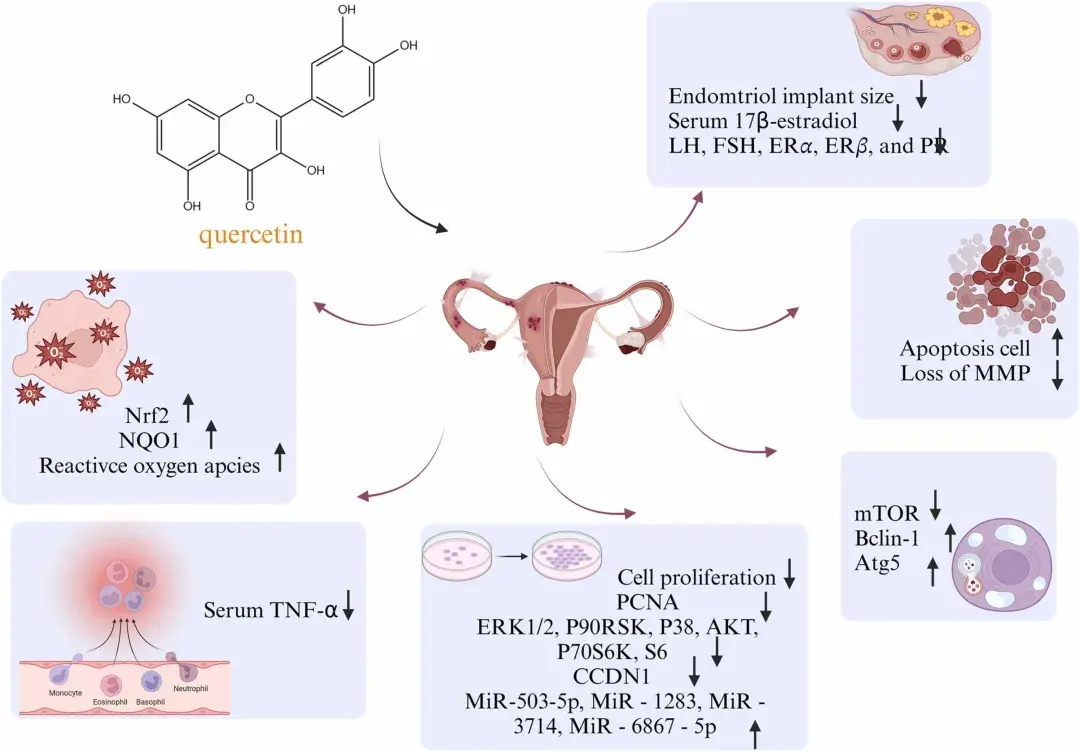
Quercetin’s diverse pharmacological properties have shown promising results in treating gynecological conditions, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), premature ovarian failure (POF), and endometriosis. Its ability to reduce oxidative stress, regulate inflammation, and improve hormonal balance makes it a valuable therapeutic option.
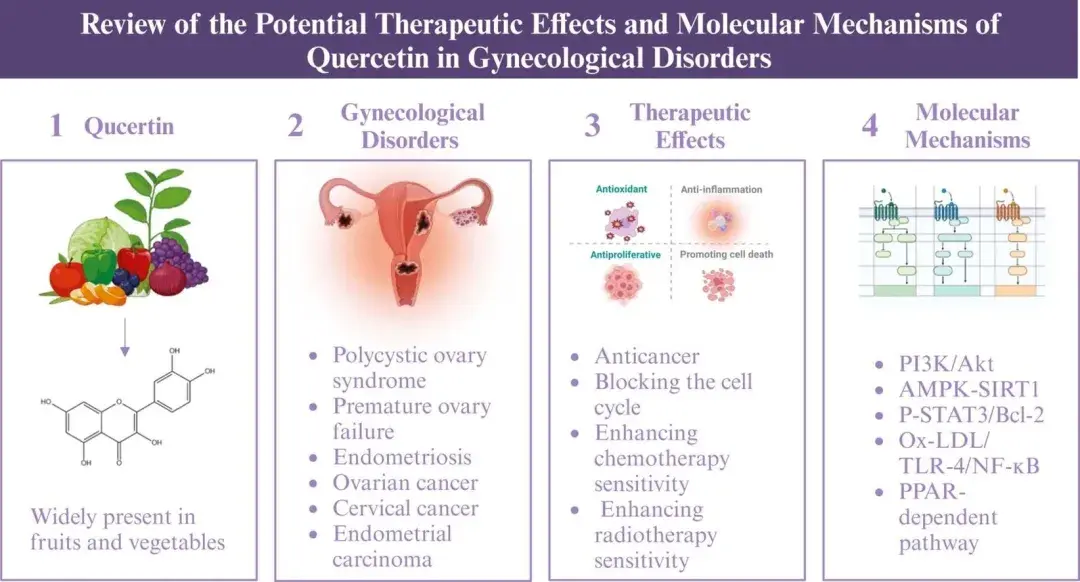
Although current studies highlight its efficacy, further research is needed to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms and confirm its safety in clinical applications.
1. Conclusion
Quercetin is emerging as a potent bioactive compound with multifaceted health benefits. From modulating epigenetic processes in cancer to regulating metabolic and inflammatory pathways in chronic diseases, quercetin holds immense potential for therapeutic use. However, challenges like low bioavailability and limited mechanistic insights call for further research to optimize its applications in functional foods, supplements, and pharmaceuticals.