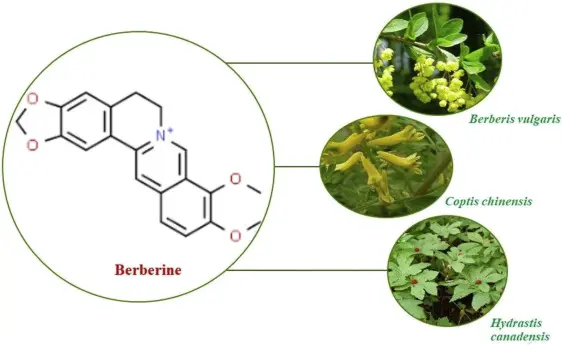
Berberine: An Ancient Remedy Finds Its Calling in Gut Health
Berberine, a natural alkaloid extracted from plants like berberis aristata or Berberis vulgaris or Phellodendron chinense, has been a cornerstone of traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, known for its characteristic bitterness. Once considered an underutilized "minor player" in modern medicine, recent research has unveiled its profound effects on gut health, metabolism, and various chronic diseases. This breakthrough has placed berberine in the spotlight as a powerful natural therapeutic agent.

1. The Journey of Berberine: From Obscurity to Recognition
Discovered in 1826, berberine remained relatively unnoticed for over a century. Despite its well-defined chemical structure in 1910, its clinical potential was not fully realized until 1979, when Chinese pharmacologist An Jingxian successfully developed it as an antibacterial drug. By 1986, berberine was approved for treating gastrointestinal infections such as bacterial dysentery and irritable bowel syndrome. Today, its applications are expanding into areas like blood sugar regulation and anti-cancer therapy.
2. Why berberine Took Time to Shine
Berberine’s delayed recognition can be attributed to its pharmacokinetic challenges. Poor oral absorption and low bioavailability limited its effectiveness in traditional contexts. When taken orally, most of the compound is metabolized and excreted before reaching systemic circulation. However, this perceived limitation turned out to be its greatest advantage, allowing berberine to interact directly with gut microbiota, leading to profound therapeutic benefits.
3. Gut Microbiota: The Key to Unlocking Berberine’s Potential
Research shows that over 70% of commonly used drugs are metabolized in the liver, but poorly absorbed compounds like berberine interact directly with gut microbiota. This interaction results in unique therapeutic effects by:
- Modulating the gut microbiome.
- Producing metabolites that influence drug efficacy.
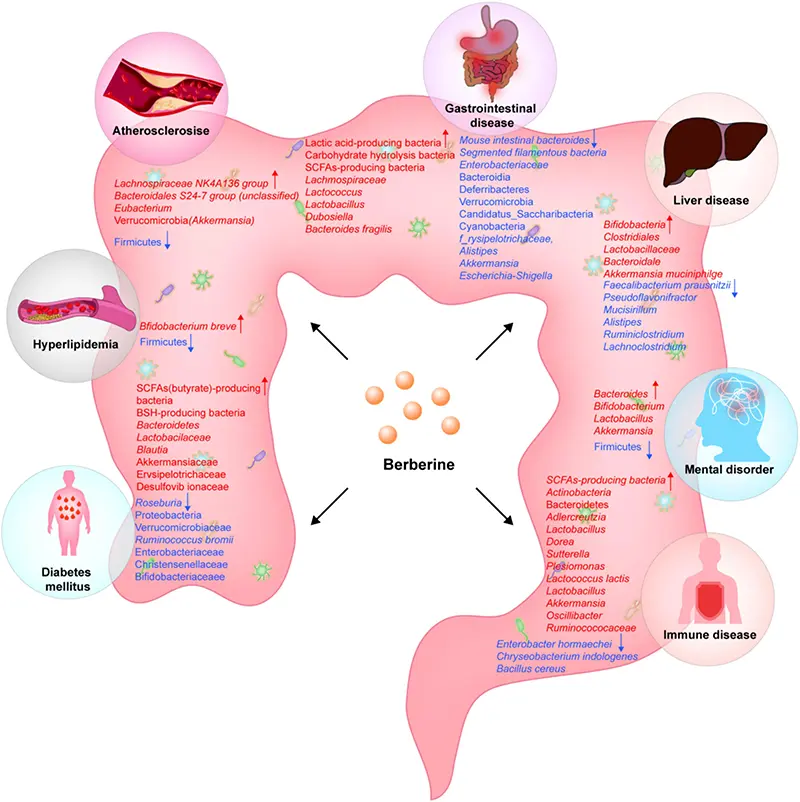
Berberine has demonstrated its ability to regulate gut flora, providing therapeutic benefits for conditions like:
- Neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Metabolic disorders such as diabetes.
- Digestive system diseases.
4. Synergy Between Probiotics and Berberine for Blood Sugar Control
Berberine’s role in regulating blood sugar highlights its profound impact on gut health. In a 2020 study by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, berberine was shown to lower blood glucose in diabetic rats by:
- Promoting the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria.
- Modulating ileal gene expression.
- Reducing systemic and pancreatic inflammation.
Additional research from BGI Research further explored the synergy between probiotics and berberine:
- 2020 Study in Nature Communications:
Berberinealtered gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism, effectively reducing blood glucose in type 2 diabetes patients. Probiotics enhanced its glucose-regulating effects in older patients, offering a new pathway for diabetes intervention. - 2021 Study on Postprandial Lipids:
A combination of probiotics and berberineimproved lipid profiles in diabetic patients by reducing total cholesterol and LDL levels. This synergy likely works through the activation of bifidobacterial genes, promoting lipid metabolism and reducing intestinal lipid absorption. - 2021 Multi-Center Trial in China:
A randomized, double-blind trial showed that combining berberinewith Bifidobacterium adolescentis led to superior glycemic control compared to berberine alone, demonstrating a synergistic "1+1>2" effect.
5. Key Considerations
Despite its promising effects, berberine remains a drug that requires professional guidance for safe use. The probiotics used in research are specific strains, and not all probiotics offer the same benefits. Caution is advised when considering berberine as part of a health regimen.
Conclusion
Berberine, once an overlooked compound, is now recognized as a natural powerhouse with applications extending from gut health to chronic disease management. Its ability to modulate the gut microbiota opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions in diabetes, lipid disorders, and more. When paired with targeted probiotics, berberine’s effects are amplified, offering an innovative approach to health and wellness. As research progresses, this "late bloomer" continues to revolutionize modern medicine.