How to Use Berberine for Weight Loss and Blood Sugar Control
Berberine, a natural compound derived from various plants, has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential benefits in weight loss and blood sugar control. Studies suggest that Berberine may help regulate metabolic processes, making it a popular choice for those seeking to enhance their weight management efforts and improve their overall health. This powerful alkaloid works by activating an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which plays a crucial role in energy metabolism and glucose regulation.
As obesity and diabetes become increasingly prevalent in today’s society, many individuals are exploring alternative solutions to support their health goals. Berberine offers a promising option due to its multifaceted approach to managing weight and blood sugar levels. It not only aids in reducing body fat but also improves insulin sensitivity, making it an appealing supplement for those struggling with weight-related issues. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the mechanisms of Berberine, practical applications for its use, and insights on how to incorporate it effectively into your lifestyle for optimal results.
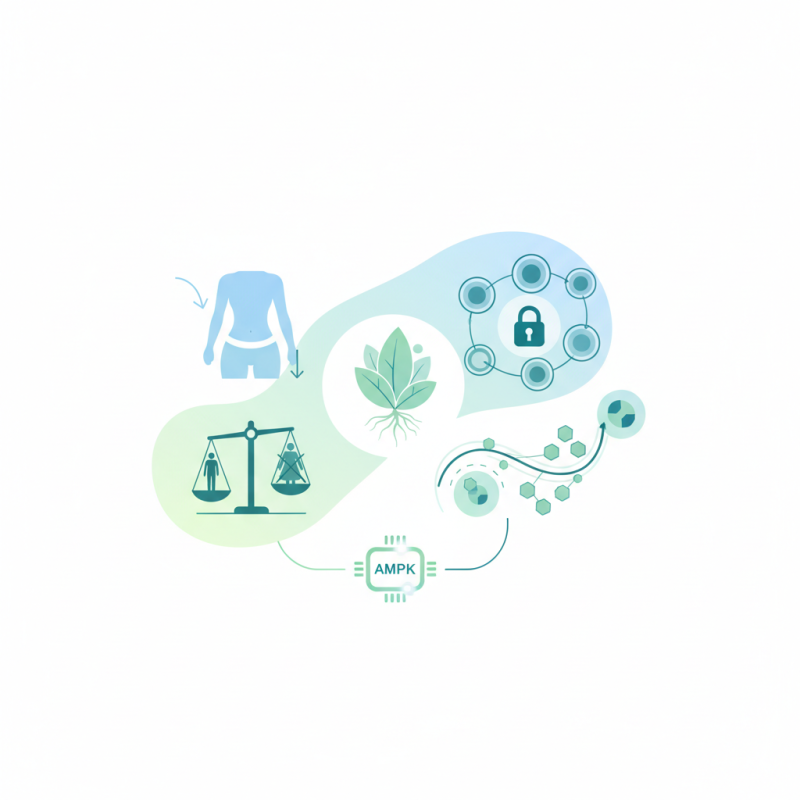

Understanding Berberine: A Natural Compound for Health Benefits
Berberine is a natural compound derived from various plants such as barberry, goldenseal, and tree turmeric. Traditionally used in Chinese medicine, it has gained attention for its potential health benefits, particularly in weight loss and blood sugar control. Berberine works by influencing several biochemical pathways in the body, which can support metabolic health. Studies suggest that it may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver, making it an appealing option for those looking to manage their weight and blood sugar levels.
Tips for incorporating berberine into your routine include starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it, as this can help minimize any gastrointestinal discomfort. It’s also beneficial to take berberine with meals to enhance its absorption and effectiveness. Additionally, pairing berberine with a balanced diet rich in whole foods can amplify its effects and contribute to overall wellness.
As you explore berberine's potential, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it aligns with your health needs and goals. Monitoring your body's response to berberine can help you optimize its benefits while making informed decisions about your health journey.
The Role of Berberine in Weight Loss Mechanisms
Berberine, a natural compound found in several plants, has gained attention for its potential role in weight loss and blood sugar control. Research indicates that berberine can activate the enzyme AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a crucial regulator of energy metabolism. When activated, AMPK can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce liver glucose production, and promote fat burning, making it a valuable ally for those looking to manage their weight and blood sugar levels effectively. A study published in the Journal of Obesity reported that participants who used berberine lost an average of 5 pounds over three months, while also witnessing significant reductions in fasting blood glucose levels.
Incorporating berberine into your regimen can be enhanced by following a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity. Tips for maximizing its benefits include taking berberine with meals to avoid gastrointestinal upset, which is a common side effect, and ensuring that the intake is coupled with a diet rich in fiber and low in refined sugars. Moreover, maintaining hydration and including regular exercise not only supports weight loss but also amplifies berberine's effects on metabolic health.
Moreover, dosage plays a critical role in berberine’s effectiveness; the research suggests a typical dose ranges from 900 mg to 1,500 mg daily. For best results, consider splitting the intake into two or three doses throughout the day. Monitoring blood sugar levels can provide additional insights into how well it’s working alongside lifestyle changes, ensuring that you’re on the right path to achieving your health goals.
How Berberine Affects Blood Sugar Levels and Insulin Sensitivity
Berberine is a compound that has garnered attention for its potential to improve blood sugar levels and enhance insulin sensitivity, making it a popular choice among those seeking to manage their weight and metabolic health. Research has shown that berberine can significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels, with studies indicating reductions of up to 20% in participants with type 2 diabetes or prediabetic conditions. According to a meta-analysis published in the journal *Metabolism*, berberine supplementation was found to be as effective as some prescription medications, such as metformin, in improving glycemic controls.
The mechanism through which berberine operates involves several pathways. It enhances insulin sensitivity by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme that plays a pivotal role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. This action not only aids in the reduction of insulin resistance but also supports weight loss efforts by promoting fat oxidation. A clinical trial published in *The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition* showed that participants taking berberine experienced not only lower blood sugar levels but also a decrease in body mass index (BMI), highlighting its dual role in managing blood sugar and body weight concurrently.
Moreover, berberine's influence on lipid metabolism adds another layer of benefit. By reducing total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, it further supports cardiovascular health. Research from the *Journal of Clinical Lipidology* highlights that berberine supplementation can lead to a significant decrease in lipid levels, thereby reinforcing its role in managing not just glucose metabolism but also overall metabolic syndrome. These findings underscore berberine's growing reputation as a natural and effective aid for weight management and blood sugar control.
Effects of Berberine on Blood Sugar Levels and Weight Loss
This chart illustrates the effects of berberine on fasting blood sugar levels and weight loss over a period of 12 weeks. Both parameters show significant improvement, indicating berberine's potential benefits for managing blood sugar and supporting weight loss.
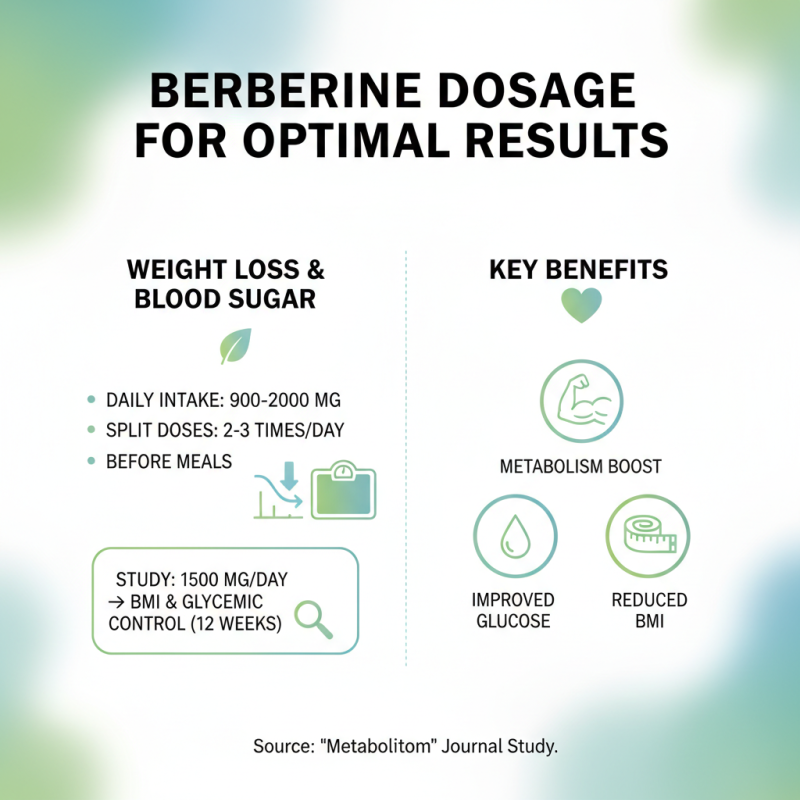
Recommended Dosage and Administration of Berberine for Optimal Results
When considering the use of berberine for weight loss and blood sugar control, proper dosage and administration are crucial for achieving optimal results. Research indicates that a daily intake of 900 to 2,000 mg of berberine, divided into two to three doses, tends to be effective. A study published in the journal "Metabolism" showed that participants who took 1,500 mg of berberine daily experienced a significant reduction in body mass index (BMI) and improved glycemic control over 12 weeks. The timing of dosages can also enhance effectiveness; taking berberine before meals may help modulate postprandial blood sugar levels.
Tips for administering berberine include starting with a lower dose, such as 500 mg per day, and gradually increasing it to assess tolerance. It’s advisable to take berberine with meals to improve absorption and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort, which is a common side effect. Additionally, pairing berberine with a balanced diet and regular exercise can amplify its weight loss effects and contribute to better blood sugar management. Tracking progress and consulting with a healthcare professional can provide further personalized adjustments to your berberine intake strategy.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Berberine
When considering the use of berberine for weight loss and blood sugar control, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects and precautions. While berberine is generally considered safe for many individuals, it can cause gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, constipation, and upset stomach, particularly when taken in high doses. Starting with a lower dosage and gradually increasing it can help mitigate these effects. Additionally, users should be aware that berberine can interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect blood sugar levels and metabolic processes, which can increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Individuals with specific health conditions, such as liver disease, should exercise caution and consult a healthcare professional before starting berberine supplementation. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also avoid berberine due to a lack of sufficient research on its safety in these populations. Overall, while berberine may offer benefits for weight management and blood sugar control, it is crucial to approach its use thoughtfully and with appropriate medical guidance to minimize any potential risks.
How to Use Berberine for Weight Loss and Blood Sugar Control - Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Berberine
| Aspect |
Details |
| Dosage for Weight Loss |
500 mg to 1500 mg per day, divided into 2-3 doses |
| Dosage for Blood Sugar Control |
500 mg to 2000 mg per day |
| Common Side Effects |
Digestive issues, diarrhea, constipation, stomach upset |
| Who Should Avoid |
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with low blood pressure |
| Interactions with Medications |
May interact with blood sugar medication, antihypertensives |
| Best Time to Take |
Before meals to optimize absorption |
| Recommended Form |
Berberine HCl capsules or powder |

About Us
Products
Nutraceuticals
Botanical Extracts
Berberis Extract
Ginkgo Biloba Extract
Rutin
Quercetin
Grape Seed Extract
European Bilberry Extract
Broccoli Seed Extract
Fisetin
Ajuga Extract
Resveratrol
Stevia Leaf Extract
Green Tea Extract
Olive Leaf Extract
Epimedium Extract
Rhodiola Rosea Extract
Panax Ginseng Extract
Pomegranate Extract
Garlic Extract
Milk Thistle Extract
Black Pepper Extract
Fruit & Vegetable Juice Powder
Customized Service
News
Blog
Contact Us